- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

A snow melting unit is a device for processing, or, in other words, melting snow and ice in urban conditions. Their use is extremely necessary in the winter season, when, after heavy snowfall, utilities take out tons of snow that need to be disposed of. For today in Moscow 48 stationary snow-melting points function. How do they work - about this in today's issue!

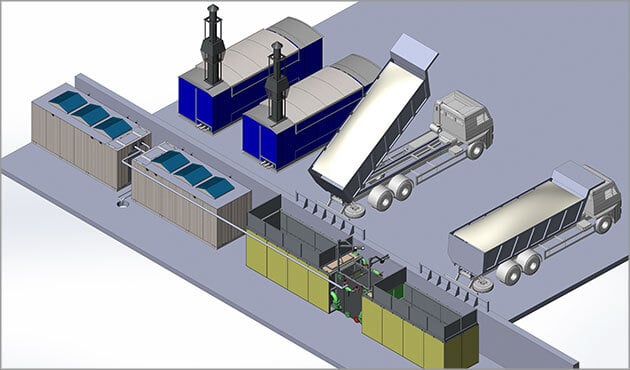
The principle of operation of any snow melting plant is based on the use of heat, which leads to the melting of snow. The installation consists of a receiving hopper or chamber, a unit for heat generation and a filtration system.
On the surface of any installation there is a grating floor, on which trucks pour snow masses. At the first stage, the primary processing of the brought snow takes place - the grates detain the largest debris. The snow-melting chamber itself is located inside the installation under the ground. It is there that there is a direct process of forced melting of snow.
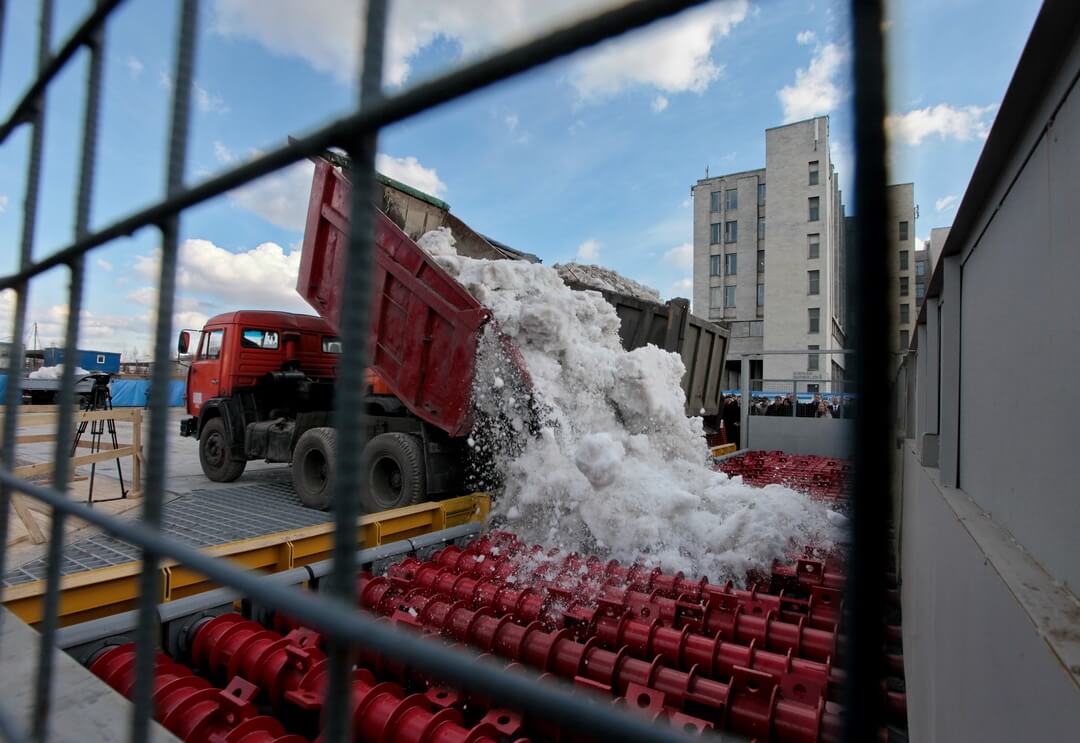

As an element for heating, a snow melting unit can use diesel or gas burners. At the same time, the hopper is divided into 2 compartments: in the first compartment, burners are placed, and in the second, snow masses are accumulated. The burners form hot gas streams and guide them through a heat exchanger, which melts solid precipitates in the chamber.
After the formation of thawed water, a special mechanism filters out the remaining debris, and the liquid passes through local treatment facilities that trap sand and other small particles and is discharged into the sewer. This makes it possible to prevent clogging of sewers.
From the moment of unloading the snow masses and until they are completely dissolved in the melting chamber, about 3-4 minutes pass. During this time, the plant is capable of processing up to 10 tons of sediment.
There is also an easier way of melting snow - with the help of running water. The snow masses are dumped into a bunker filled with hot water, in which it naturally melts. At the same time, snow is constantly mixed with incoming running water, heated to eighteen, and sometimes thirty degrees. As the snow masses are thrown into the smelter, the water level in the bunker rises. Excess water passes through vertical drainage pipes and filters and then merges into the sewage network.
Stationary snow melting stations are often combined with heating channels and sewerage, which allows to optimize the operation of the equipment.
In addition to stationary installations, there are mobile stations. They work on the same principles, but because of the dimensions they can melt smaller amounts of snow: about 90 cubic meters per hour against 300. The average operating time of such a melting plant without refueling is about eight hours.
The article is based on materials .
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment