- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Electronic paper was first developed at the Xerox Research Center in Palo Alto by Nick Sheridon in the 1970s. The first electronic paper, called Girikon, consisted of polyethylene spheres from 20 to 100 microns in diameter. Each sphere had a negatively charged black and a positively charged white half. All spheres were placed in a transparent silicone sheet, which was filled with oil to allow the spheres to rotate freely. The polarity of the applied voltage to each pair of electrodes determined which side the sphere would turn, thereby giving the white or black color of the dot on the display.

In the 1990s, Joseph Jacobson invented another type of electronic paper and founded the corporation E Ink, which, together with Philips, brought this technology to the market. How does a modern E-Ink-display work? This is in today's issue!

The active layer of the E-Ink display contains miniature transparent capsules with black and white particles (pigments). Black and white particles respond differently to the appearance of an electrical potential: positively charged white particles are attracted to negatively charged electrodes, and negatively charged black particles to contacts having a positive charge. In this case, the microcapsules with the pigment are very small - their diameter is comparable to the diameter of a human hair. In the neutral state, white and black particles are inside the microcapsules in an arbitrary position. But when a certain area of the screen is given a positive electric charge, in all the microcapsules in this section the white particles move to the front part. And black stretches an electric field on the back side of microcapsules, thereby hiding from the eyes of the user. As a result, the display shows a white spot - a pixel point of white color. If you change the polarity of the applied electrical potential, the black pigment particles will appear on the front side of the capsules, and the white particles on the back side. And at the same place the display will show a black spot.
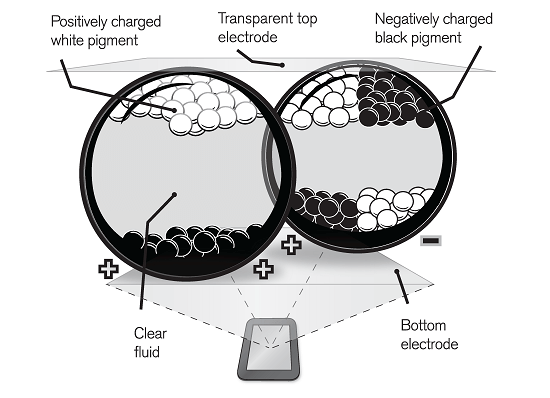
E-Ink displays use an active matrix, similar to those that are installed in LCD and OLED displays. This allows you to create large and complex images on the electronic ink screen.
In addition to monochrome E-Ink displays, there is also a multicolor electronic paper. It consists of thin colored optical filters that are added to the monochrome display. The set of points is divided into triads consisting of three colors: cyan, magenta and yellow. Unlike LCD and OLED displays, where red, green and blue colors are used and their addition, in E-Ink colors are formed by subtraction, as in printing.

The advantage of E-Ink technology is the battery life, which compares favorably with devices with LCD and OLED displays. The fact is that the display based on electronic paper consumes energy only when changing the displayed information, while the LCD display consumes energy constantly. However, E-Ink displays have a very long update time compared to LCD displays. This does not allow you to display complex interactive elements of the interface. Another drawback is the susceptibility of some E-Ink screens to mechanical damage.
The article is based on materials .
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment